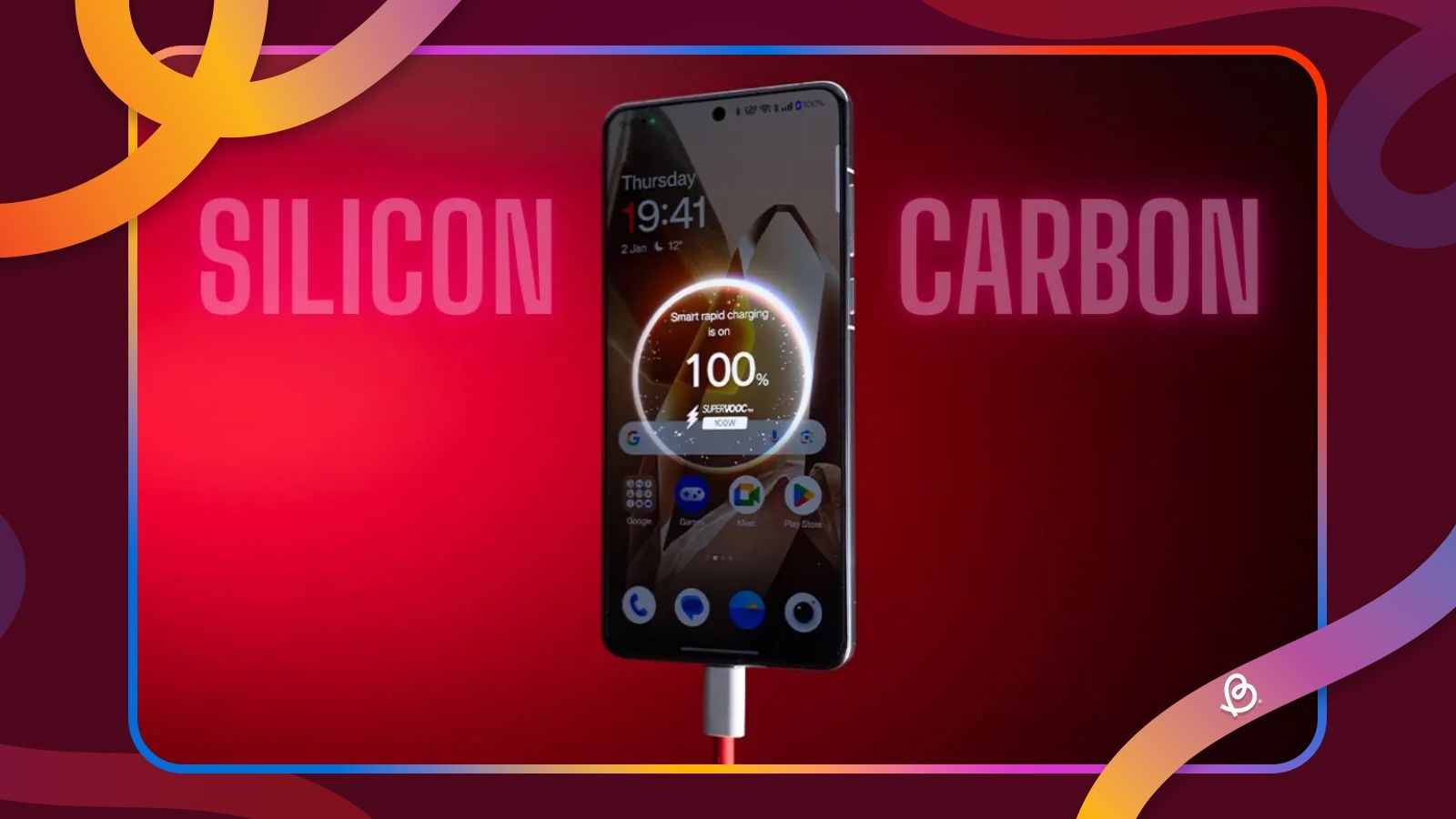
Smartphone battery trends have shifted massively from Lithium-ion batteries being the sole battery technology powering devices for over thirty years, to Silicon Carbon batteries. This is because Lithium-ion effectively hit a saturation point in terms of capacity. But how do Silicon Carbon batteries address the issue, and how do they keep the same battery life while making the phone much slimmer? Buckle up as we explain what a Silicon Carbon battery is in detail.
How is Silicon Carbon battery different?
Functionally, a Silicon Carbon battery operates on the same fundamental principles as a traditional Lithium-ion cell. It still relies on the movement of ions between a cathode and an anode to generate power. Just like in a Lithium-ion battery, the cathode in a Silicon Carbon battery is made out of Lithium Cobalt Oxide. However, the main difference lies in the anode material.
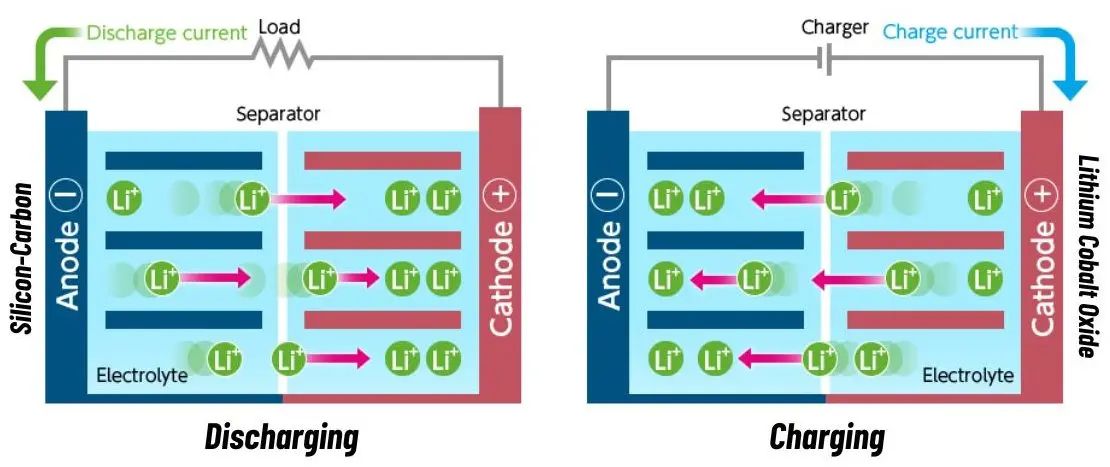
You see, traditional Li-ion batteries use Graphite anode. In this structure, Lithium ions slide between graphene layers. However, like every element, graphite has a limit to how many lithium ions it can hold. And it exists in a 1:6 ratio.
Silicon Carbon battery, on the other hand, replaces the graphite anode with a Silicon-Carbon composite. Silicon is far more efficient at storing energy and is capable of holding 15 lithium atoms for every 4 silicon atoms. This makes Silicon much denser and capable of holding more power while taking the same amount of space.
The Density Advantage in a Silicon-Carbon battery
This atomic efficiency translates to a massive jump in energy density. While standard Li-ion batteries top out at a theoretical density of roughly 387 Wh/kg, Silicon Carbon batteries can reach 600 Wh/kg. In real-world terms, this allows them to store 40% or more charge in the same physical volume. And with rapid enhancements in technology, this number is bound to increase.

For example, a battery cell that would normally be capped at 5,000mAh using a standard Li-ion cell could hold close to 8,000mAh or higher using Silicon Carbon technology, without increasing its physical dimensions. Take the Honor WIN, for example. Measuring just 8.3 mm, the smartphone boasts a 10,000mAh battery, all thanks to Silicon Carbon battery.
Now, if you ask why pure Silicon can't be used to hold more charge, it's because while it's more potent, it suffers from rapid physical expansion that damages the battery. The Carbon in the composite acts as a stabilising agent to prevent this issue. It also acts as an enabler of faster charging, which we will touch on later
Benefits of Modern Smartphones using Silicon-Carbon battery
The primary benefit is, of course, the size-to-power ratio. Because the silicon-carbon composite is denser, manufacturers can avoid the bulk associated with large batteries. This leads to:
- Slimmer Form Factors: As stated earlier, brands can increase the battery capacity while shrinking the device thickness. A great example of this would be the Oppo Find N5, where Oppo managed to increase the battery capacity by 15% from its predecessor, while reducing the device's thickness to just 4.21 mm when unfolded.
- Efficient Fast Charging: The absence of graphite layers in the Silicon Carbon anode allows for more efficient energy transfer. These batteries can support fast charging speeds of 80W and upward, whereas traditional Lithium-ion graphite batteries often require a multi-cell configuration to achieve similar speeds safely.
Besides, like a Li-ion battery, Silicon Carbon battery is capable of maintaining a healthy lifespan of over 1,000 charge cycles, don't suffer from memory effect and remain lightweight.
While Chinese manufacturers like OnePlus, Xiaomi, and Oppo are aggressively rolling out and improving their Silicon Carbon cells, the industry heavyweights are moving more slowly. It will likely take another year or two for this technology to reach Google Pixel and Samsung Galaxy smartphones.
Finally, don't mistake Silicon Carbon tech for a perfect eco-friendly solution. While Silicon is found in abundance, these batteries still rely on the same water-intensive extraction of Lithium and Cobalt as their predecessors. Silicon Carbon battery solves the density problem, but it doesn't really solve the dirty reality of battery production.