Qualcomm's budget processors are regarded as some of the best in the business, with processors like the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 and 6 Gen 4 aiming to strike a good balance between performance and efficiency. The "s" moniker suggests a slightly toned-down version of the processor, but in the case of the latest Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 and last year's Snapdragon 6s Gen 3, the story is a bit different. We pitted the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 and Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 against each other, and the difference is shockingly high.
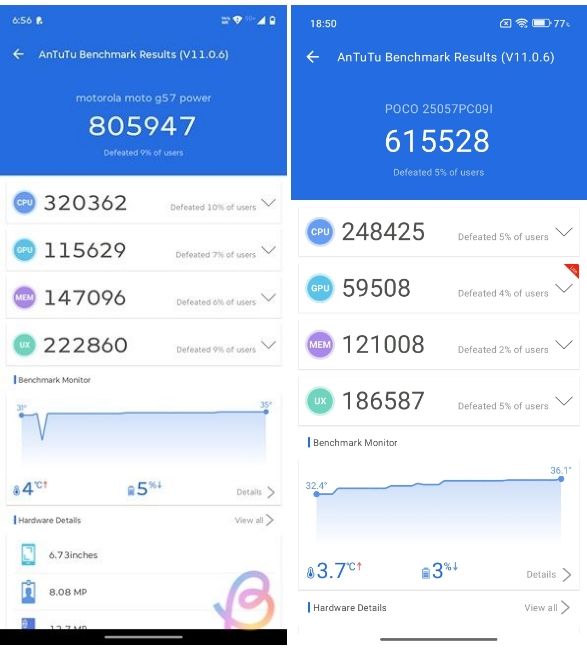
Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 vs Snapdragon 6s Gen 3: AnTuTu Score
| AnTuTu Benchmark | Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 | Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 |
|---|---|---|
| AnTuTu Score | 805,947 | 615,528 |
| CPU | 320,362 | 248,425 |
| GPU | 115,629 | 59,508 |
| Memory | 147,096 | 121,008 |
| UX | 222,860 | 186,587 |
In our testing on the Moto G57, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 managed to score 805,947 points compared to the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3's 615,528 points in the Poco M7 Plus. That's a 30% increase in overall performance, meaning the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 is objectively the better processor of the two.
The main difference is in the GPU, as the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 scores 115,629 points, decimating the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3's 59,508 points. The score is pretty close to Dimensity 7300, and makes the 6s Gen 4 the better gaming chipset. However, it's only comparatively better, as 115,629 points are still considered very low for a GPU score.
The difference in performance is due to the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 using twice as many performance cores as the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3, clocked at 100 MHz higher speeds. With 4x Cortex-A78 clocked at 2.3 GHz and 4x Cortex-A55 clocked at 2.0 GHz, the 6s Gen 4 is bound to perform significantly better in both single and multi-core. Not to mention, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 is built on a 4nm process vs 6nm of the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3.
Besides, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 also boasts a better Adreno 719 GPU, support for faster memory and UFS 3.1 storage. It fails to reach its full potential here as the Moto G57 only has UFS 2.2 and uses older LPDDR4X RAM. All in all, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 is the clear winner when it comes to raw performance.
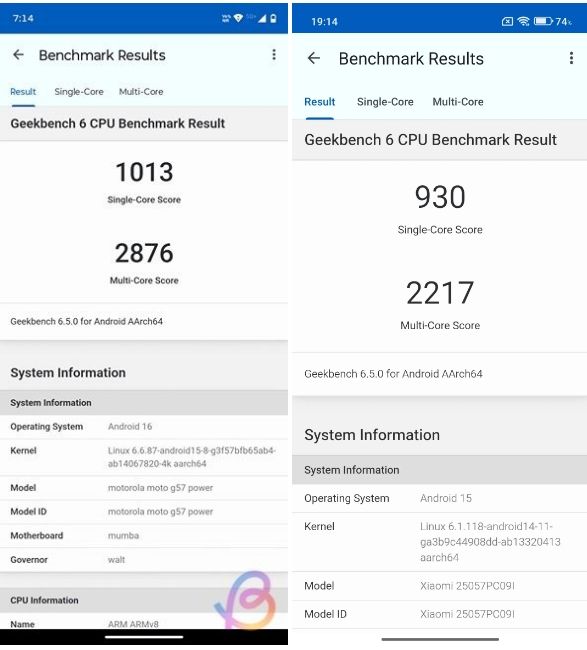
Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 vs Snapdragon 6s Gen 3: Geekbench Score
| Geekbench 6 CPU | Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 | Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Single-core | 1,013 | 930 |
| Multi-core | 2,876 | 2,217 |
The difference in single and multi-core scores is all thanks to the two more Cortex-A78 cores clocked 100 MHz higher. As a result, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 breaks the 1,000 barrier in single-core (1,013 vs 930), offering slightly better execution speeds.
The difference is much bigger in multi-core, with the 6s Gen 4 scoring 2,876 points and the 6s Gen 3 scoring 2,217 points. That's a 23% difference, indicating the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 will handle multitasking and heavy applications much faster than its predecessors.
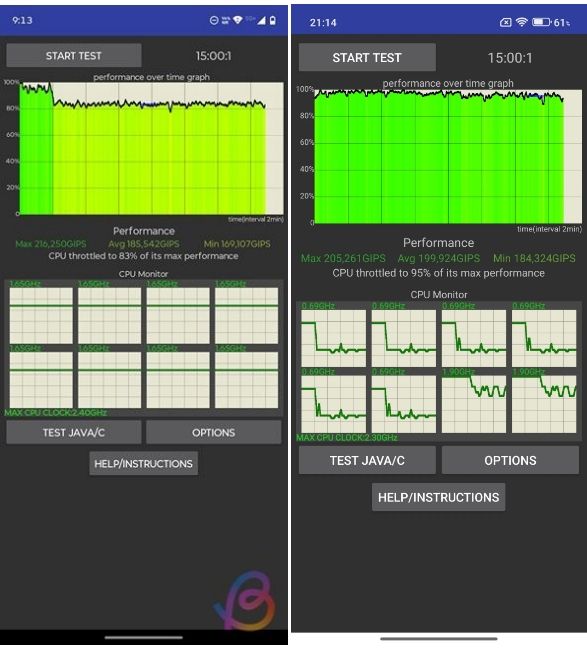
Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 vs Snapdragon 6s Gen 3: CPU Throttling
| CPU Throttling Test | Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 | Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Score | 216,250 GIPS | 205,261 GIPS |
| Average Score | 185,542 GIPS | 199,924 GIPS |
| Minimum Score | 169,107 GIPS | 184,324 GIPS |
| Throttling Percentage (Higher is better) | 83% | 95% |
This is where the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 shines. While the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 has a higher peak performance (216k vs 205k), it throttles down to 83% relatively quickly. In contrast, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 is rock solid. It throttles only to 95% and actually maintains a higher average performance of 199,924 GIPS over the 15-minute test than the 6s Gen 4, which scores 185,542 GIPS.
This could be due to the newer 4 nm Samsung process being far less efficient, which has historically been an issue with Samsung's manufacturing. Therefore, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3, although older, is more consistent for sustained CPU workloads, even if its burst speed is slightly lower.
Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 vs Snapdragon 6s Gen 3: 3DMark Score
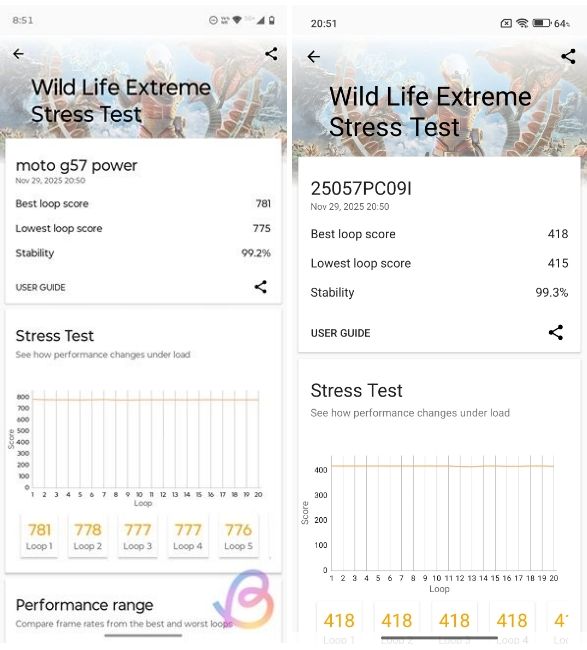
| 3DMark Wild Life Extreme Stress Test | Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 | Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Best Loop Score | 781 | 418 |
| Lowest Loop Score | 775 | 415 |
| Stability | 99.2% | 99.3% |
The 3DMark results confirm the AnTuTu GPU results. The Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 scores 781 points, which makes it almost 46% faster than the 6s Gen 3's score of 418. This is all thanks to the better Adreno 710 GPU, which is significantly faster than the Adreno 619. However, it's much slower than the GPU found in the Snapdragon 6 Gen 4.
Both chips, however, show excellent stability of over 99%, meaning neither suffers from thermal throttling during graphics-intensive tasks. Still, if you're a gamer, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 is objectively the better choice.
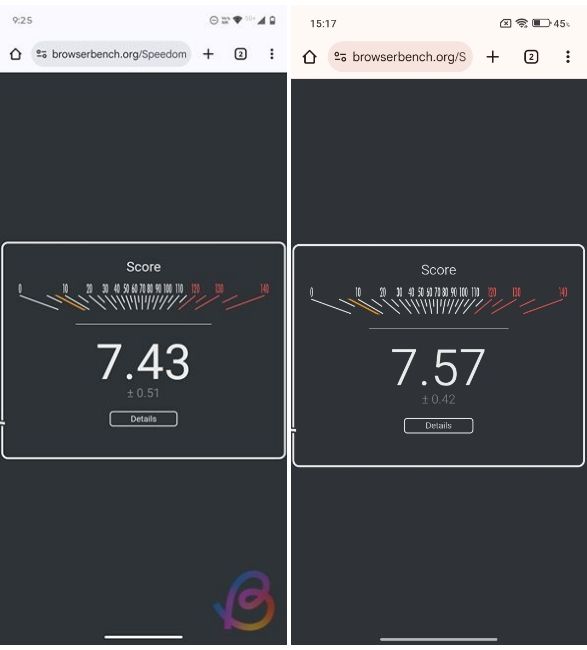
Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 vs Snapdragon 6s Gen 3: Speedometer 3.0 Score
The Speedometer performance on both chips is well within the margin of error. The Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 scores 7.43 while its predecessor scores a slightly higher 7.57 points. Both aren't great and will be slow to load a JavaScript-heavy webpage, but they're both more than capable of browsing web pages.
Benchmark Gallery
Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 vs Snapdragon 6s Gen 3: Specs Comparison
| Specs | Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 | Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Process Node | Samsung 4nm (4LPX) | TSMC's 6nm |
| CPU | 8-core Kryo CPU | 8-core Kryo CPU |
| CPU Cores | 4x 2.4 GHz (Cortex-A78), 4x 1.8 GHz (Cortex-A55) | 2x 2.3 GHz (Cortex-A78), 6x 2.0 GHz (Cortex-A55) |
| GPU | Adreno 710 GPU | Adreno 619 |
| Storage and Memory | UFS 3.1, LPDDR5X memory, Up to 3.2 GHz | UFS 2.2, LPDDR4X up to 2.3 GHz |
| NPU | Hexagon NPU | Qualcomm Hexagon NPU |
| ISP | Dual 12-bit ISP, 200MP photo capture, 2K HDR video at 30 FPS | Qualcomm Spectra Triple ISP 12-bit with 108 MP camera and 1080p recording at 30 FPS |
| Modem | Snapdragon Release 16 5G modem, Peak download speed up to 2.9 Gbps | Snapdragon X51 5G, Peak Download speed of up to 2.5 Gbps |
| Connectivity | Wi-Fi 6E, Bluetooth 5.4 | Wi-Fi 5 and Bluetooth 5.2 |
Verdict
The Snapdragon 6s Gen 4 is a significant upgrade over its predecessor. It games better, has better CPU speeds, making it a clear winner for users who want maximum performance. However, the Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 is slightly more efficient. It beats the newer chip in sustained performance and shows that it remains a very capable and stable processor for daily use.
























.jpg)


